The Kochava attribution engine is comprehensive, authoritative and actionable. The system considers all possible factors and then separates the winning click from the influencers in real-time. The primary elements of engagement are impressions, clicks, installs and events. Each element has specific criteria which are then weighed to separate winning engagements from influencing engagements.
(see iOS 14+ restrictions)
Engagements
Kochava collects (via momentary redirect or network server ping) device information when an impression is served or a user clicks on an advertisement served by a network. Each of these engagements are eligible for attribution. This collected device information ranges from unique device identifiers to the IP address of the device at the time of click or impression, dependent upon the capabilities of the network.
Kochava has thousands of unique integrations. Through the integration process, we have established which device identifiers and parameters each network is capable of passing on impression and/or click. The more device identifiers that a network can pass, the more data is available to Kochava for reconciling clicks to installs. When no device identifiers are provided, Kochava’s robust modeled attribution logic is employed which relies upon IP address and device user agent. The integrity of a modeled match is lower than a device-based match, yet still results in over 90% accuracy.
The Kochava system also determines whether a device has previously engaged with an advertisement. When multiple engagements of the same type occur, they are identified as duplicates to provide advertisers with more insight into the nature of their traffic.
Kochava tracks every engagement with every ad served, which sets the stage for a comprehensive and authoritative reconciliation process.
Installs
Once the app is installed and launched, Kochava receives an install ping (either from the Kochava SDK within the app, or from the advertiser’s server via Server-to-Server integration). The install ping includes device identifiers as well as IP address and the user agent of the device. The data received on install is then used to find all matching engagements based on the advertiser’s settings within the Postback Configuration and deduplicated. For more information on campaign testing and device deduplication, refer to our Testing a Campaign support document.
Events
The advertiser has complete control over the implementation of tracking events within the app. In the case of reconciliation, the advertiser has the ability to specify which post-install event(s) define the conversion point for a given campaign. The lookback window for event attribution within a reengagement campaign can be refined within the Tracker Override Settings. If no reengagement campaign exists, all events will be attributed to the source of the acquisition, whether attributed or unattributed (organic).
Reconciliation Factors
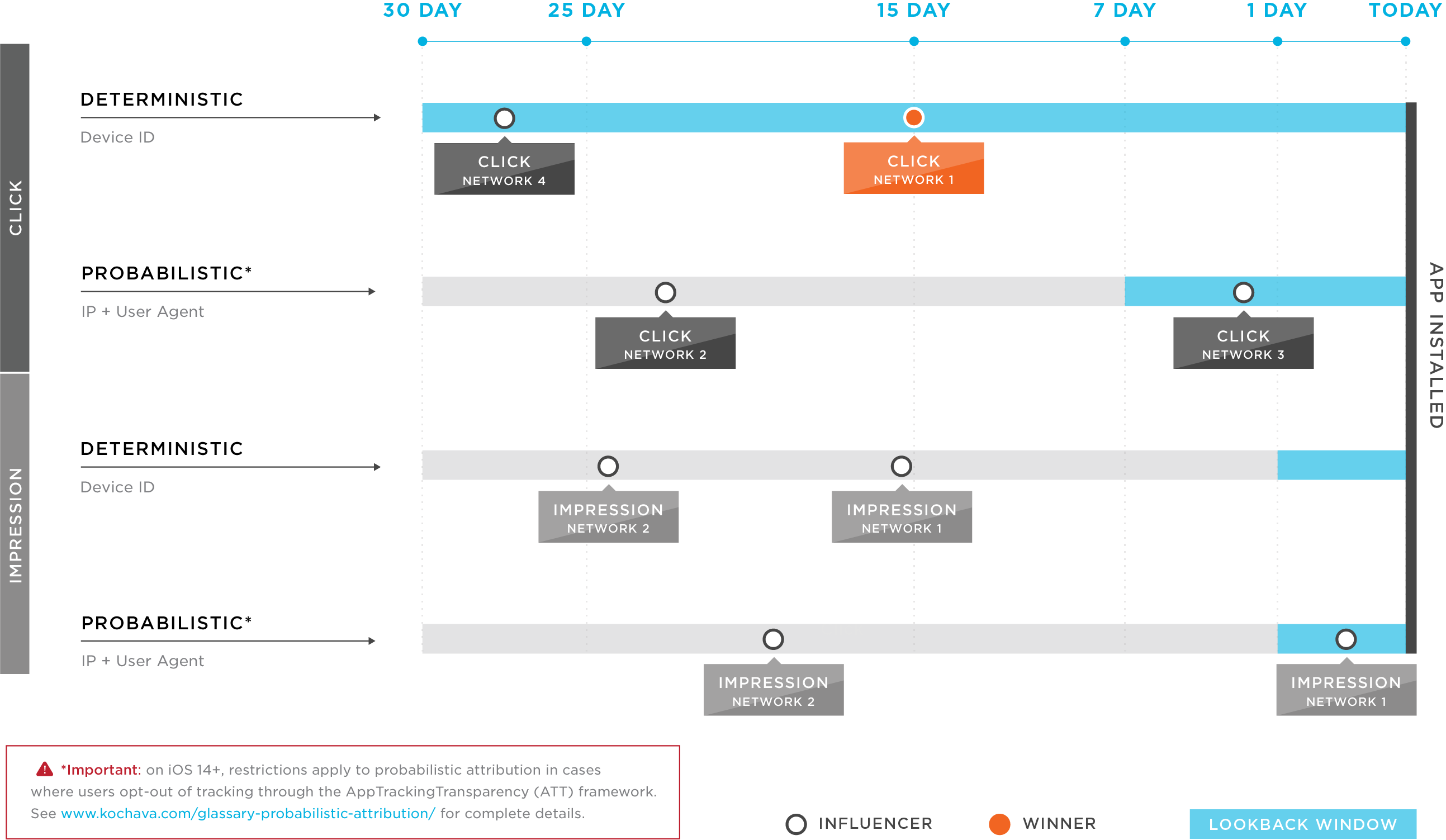
Priority 1 — Lookback Window
Priority 2 — Match Integrity
Priority 3 — Click Time
Lookback Window:
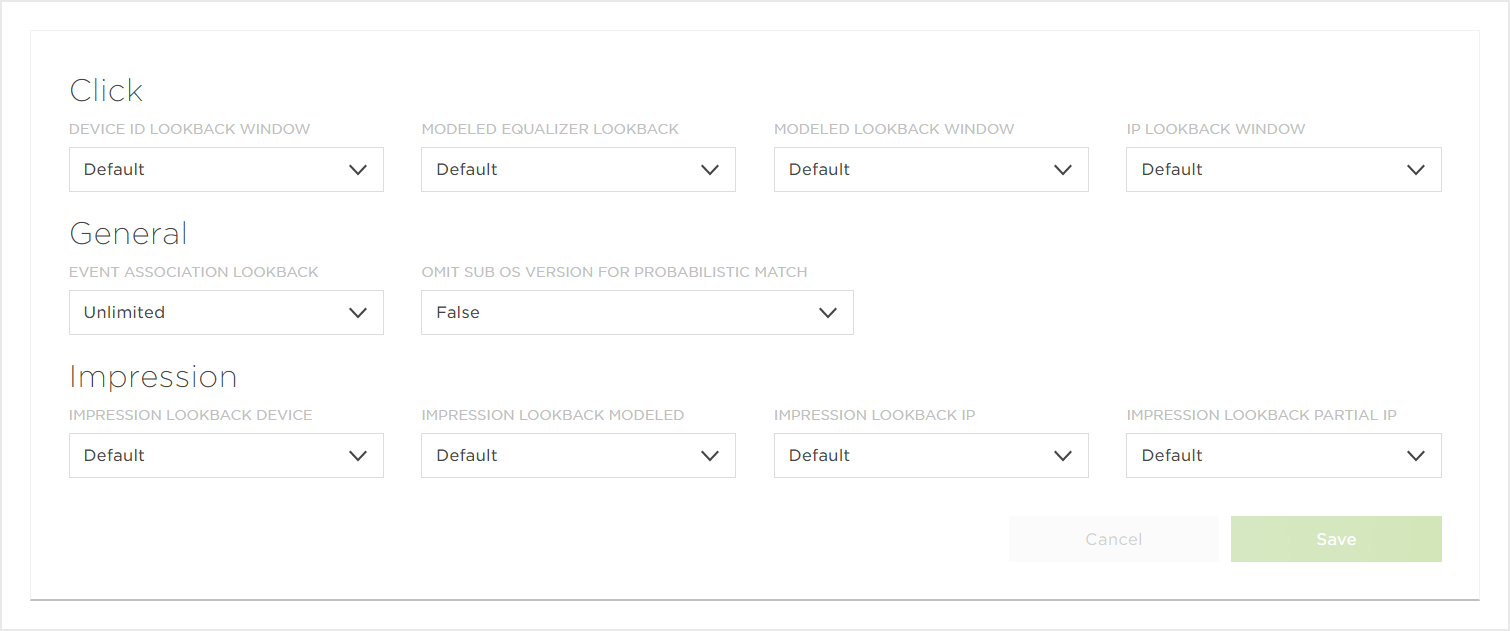
The lookback window defines how far back, from the time of install, to consider engagements for attribution. There are different lookback window configurations for device and modeled matches for both clicks and installs.
NOTE: A lookback window of one day means that the click must have been recorded <24 hours before the install.
The lookback window is configurable within the Tracker Overrides section of the Kochava UI. The lookback windows for SANs is defined within the partner UI.
Match Integrity —
Kochava’s reconciliation system works in a waterfall format. The attribution for an install is made against clicks and impressions in the following order of priority:
Click Matching —
Clicks have a higher priority for attribution than impressions
- Device-Based Matches (equally weighted examples below)
- Self-Attributing Network (SAN) claims including Facebook, Twitter, Apple Search Ads and Google
- Device ID (including progressive reconciliation)
- Google Referrer
- Standard Modeled (IP Address + User Agent)
- No Device ID present on click
- Unmatched Device ID present
- IP-Only Modeled
- No Device ID present on click
- Unmatched Device ID present
- IP Range-Only Modeled
- No Device ID present on click
- Unmatched Device ID present
Impression Matching —
After click matching has been attempted, all unattributed installs are subject to impression matching.
- Device-Based Match
- Completed View (this is an impression type, defined by each network, often referring to a completed video view)
- All other impression types (any other tracked impressions)
- Standard Modeled
- Completed View (this is an impression type, defined by each network, often referring to a completed video view)
- All other impression types (any other tracked impressions)
- IP-Only Modeled
- Completed View (this is an impression type, defined by each network, often referring to a completed video view)
- All other impression types (any other tracked impressions)
- IP Range-Only Modeled
- Completed View (this is an impression type, defined by each network, often referring to a completed video view)
- All other impression types (any other tracked impressions)
Time of Engagement —
The final criteria for reconciliation is the time of the click or impression. When all other factors are equal, the last engagement wins the attribution.
